Lab 06 - Sensors fusion: using multiple sensors for autonomous drive
Robotics II
Poznan University of Technology, Institute of Robotics and Machine Intelligence

Laboratory 6: Sensor fusion I - using multiple sensors for autonomous drive
Back to the course table of contents
The goal of the laboratory is to develop a way to extract depth information from many visual sensors.
Pre-work activities
Download the rosbag recording and copy it into the docker container.
Keep a ROS engine alive.
roscorePlay the recording and check its content using both
rvizandrostopictools.rosbag play depth.bag -r 0.5
1. Depth sensor
Depth cameras (RGB-D) allow to obtain information about the real distance of objects from the sensor and to combine this information with the RGB image indicating the corresponding pixels. These cameras are mainly used in indoor environments: robotics (movie) and augmented reality (movie).
Task
An vision_depth_detector.py program has been drafted.
Your task is to fill in missing code in the
camera_depth_callback method. Missing code is responsible
for filtering outstanding values, depth normalising and applying the
colour map. Steps: * change values larger than 15 m to 0 * change values
lesser than 3 m to 0 * rescale values to <0,256) range * convert the
matrix to the np.uint8 type * use cv2.applyColorMap in
order to colouring image (you can choose your favourite palette here)
Pay attention to np.frombuffer function that this time
it required np.float32 type to capture depth image.
Run visualization and check your work
roslaunch fsds_roboticsII vision_depth.launch
As a result, upload a screenshot with a depth image from the rviz tool to the eKursy platform.
2. Stereo-vision depth estimation
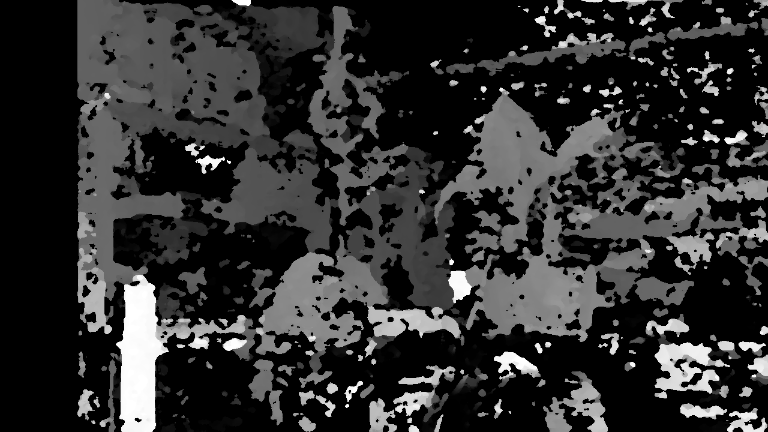

The main idea of solving for depth using a stereo camera involves the concept of triangulation and stereo matching. The formal depends on good calibration and rectification to constrain the problem so that it can be model on a 2D plane. An example of stereo depth estimation using the HITNET model.
Task
In this task, you work in the vision_stereo_detector.py
file. Inside VisionDetector class constructor is little
change. There are two subscribers for the left and right camera and they
are connected by ApproximateTimeSynchronizer whose role is
to keep both images synchronous.
- In the class constructor, create
cv2.StereoSGBM_createinstance. It is an algorithm to estimate the disparity between two images. Create it with params::- minDisparity = 1
- numDisparities = 64
- blockSize = 11
Issue: the real-life cases required additional steps for using depth estimators. Due to the simulator’s behaviour, we can skip the process of camera calibration and remapping image distortions. You can find example here.
Code the
depth_estimationmethod following instructions:- convert left and right image to grayscale
- compute the depth image using
.compute(left_image, right_image)method - change values lesser than 50 to 0
- change values larger than 300 to 0
- rescale values to <0,256) range
- convert the matrix to the np.uint8 type
- use
cv2.applyColorMapin order to colouring image (you can choose your favourite palette here)
Run visualization and check your work
roslaunch fsds_roboticsII vision_stereo.launch
As a result, upload a screenshot with a stereo depth image from the rviz tool to the eKursy platform. Additionally, comment on the visible differences between depth images and stereo-depth images.
3. Calculate truth cones depth based on range image
Download the rosbag recording and copy it into the docker container.
Play the recording and check its content using both
rvizandrostopictools.rosbag play depth_boxes.bag -r 0.75
Task
The task is to generate a Pose object for each bounding box. The rosbag contains the following topics: left image, depth image and bounding box array.
Your workspace file is vision_pose_estimator.py and you
can launch it using:
roslaunch fsds_roboticsII vision_pose_estimator.launch
Your subtasks are: * in the estimate_cones_poses
function get the depth value of the centre of the box * tip: check the
vision_msgs/BoundingBox2D message documentation * tip:
remember that python indexes must be an integer * in the
subsciber_callback function: * Split cone_poses into three
parts: red_cones, yellow_cones,
blue_cones. Each value of cone_poses is a tuple:
category and Pose. New lists should contain
only Pose values. * Below, inside the for-loop add function
which drawing cones rectangles with respect to colours.
As a result, upload a screenshot with a image and Pose position from the rviz tool to the eKursy platform.